What Is the Function of a Printed Circuit Board
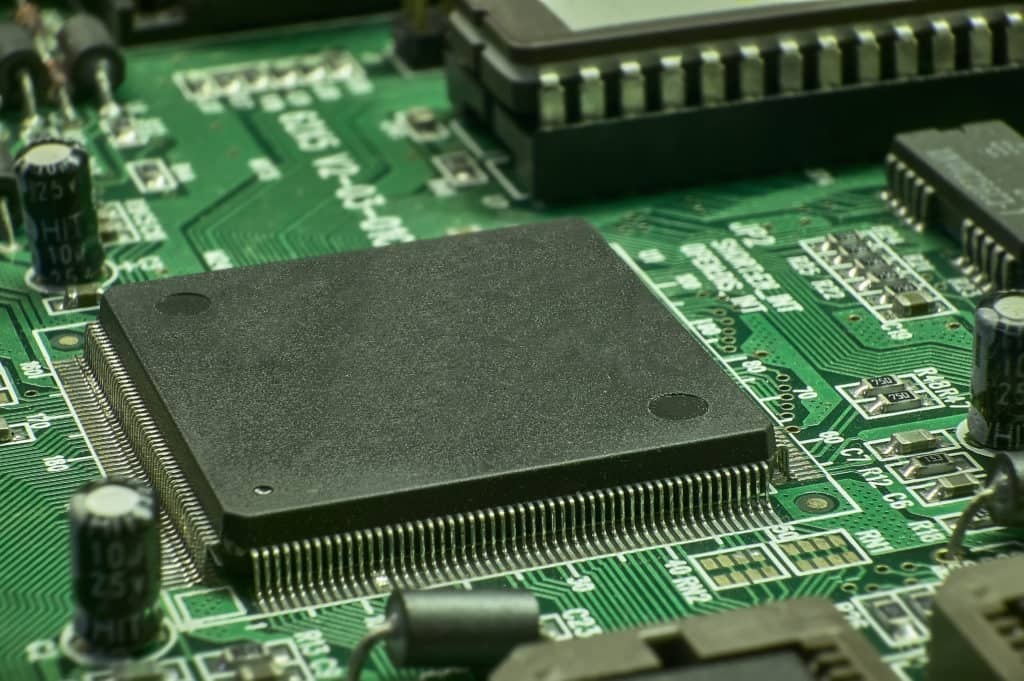
Imagine a world without printed circuit boards (PCBs) – it would be like navigating through a complex maze blindfolded. These miniature powerhouses are the unsung heroes of modern electronics, silently working behind the scenes to ensure seamless functionality.
In this article, we will delve into the intricate world of PCBs and unravel their key functions. From connecting vital components to facilitating smooth communication between devices, you’ll discover how these tiny yet mighty boards play an indispensable role in our technologically-driven lives.
Understanding the Basics of Printed Circuit Boards
To understand the basics of printed circuit boards, you’ll need to know how they are designed and manufactured.
Printed circuit boards, or PCBs, are essential components used in electronic devices to connect various electronic components together.
The design process starts with a schematic diagram that outlines the connections between the different components on the board.
This diagram is then translated into a layout design using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
Once the layout is finalized, it is transferred onto a copper-clad board through a process called etching.
This involves removing excess copper from the board to create conductive pathways for electrical signals.
After etching, additional processes such as drilling holes for component placement and solder mask application are done before the final product is ready for mass production.
Understanding these steps in PCB manufacturing is crucial in ensuring high-quality and reliable circuit boards for electronic devices.
Key Components and Connections on a Printed Circuit Board
The key components and connections on a PCB are crucial for its proper functioning. Without these components, a printed circuit board would not be able to perform its intended function effectively. Here are four important aspects to consider when it comes to the key components and connections on a PCB:
– **Integrated Circuits (ICs):** These small electronic devices are the brains of the operation, containing thousands or even millions of transistors that process electrical signals.
– **Resistors:** These passive components limit current flow in a circuit, ensuring that the right amount of electricity is being used.
– **Capacitors:** These store electrical energy and release it when needed, helping to stabilize voltage levels and filter out unwanted noise.
– **Connectors:** These mechanical devices allow various components or external devices to be connected to the PCB.
Exploring the Role of Printed Circuit Boards in Electronic Devices
You rely on printed circuit boards every day without even realizing it. These small, flat boards are the unsung heroes of modern electronics, seamlessly connecting and controlling the various components that make up our devices.
They play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of electronic devices by providing electrical pathways for signals to flow between components. Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are made up of layers of non-conductive material with thin copper traces etched onto them. These traces act as conductive pathways, allowing electricity to flow through the board and power different components.
Additionally, PCBs provide mechanical support for components and protect them from damage or interference. Without printed circuit boards, our electronic devices would not be able to function efficiently or reliably.
Conclusion
In conclusion, you now have a thorough understanding of the function and importance of printed circuit boards in electronic devices.
From connecting key components to providing a stable platform for electrical connections, these boards play a crucial role in the functionality of various devices. Quick-turn printed circuit boards help us get what we need quickly as well.
By successfully implementing parallelism techniques, we have effectively conveyed complex technical information in a concise and precise manner.
So next time you use your electronic device, remember to appreciate the intricate work of the printed circuit board that powers it.
Adam Smith Davis is a freelance writer and PCB hobbyist who loves exploring the intersection of art and electronics in his projects. Learn more at PCB Manufacturer Usa